Quercus coccinea
Scarlet Oak
Fagaceae
ExpandHabitat
- native to eastern and central United States
- zone 4
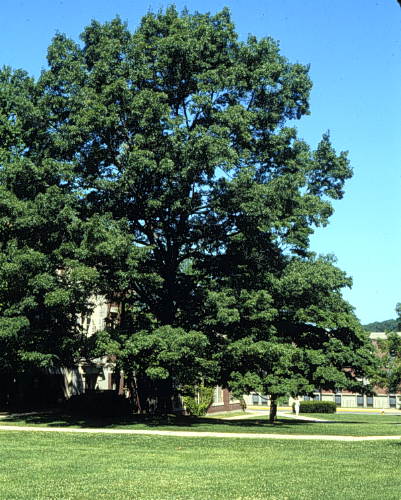
Habit and Form
- a large, deciduous tree
- 75' tall and 45' wide
- upright to rounded shape at maturity
- young plants are loosely pyramidal in shape
- upright spreading branches
- old trunk can develop an irregular loose and open crown
Summer Foliage
- alternate leaf arrangement
- 3" to 6" long by 2.5' to 4.5" wide
- seven lobes per leaf each with a bristle-tip
- shiny dark green color
- sinuses between lobes are "C"-shaped
Autumn Foliage
- most trees develop good color
- russet to scarlet
- color develops very late in fall
- can be spectacular
Flowers
- male flowers are catkins
- monoecious
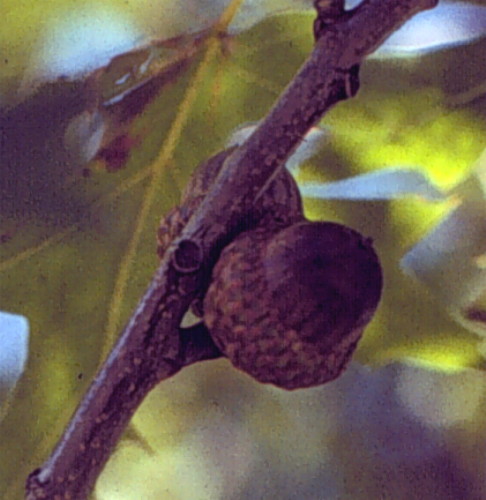
Fruit
- acorn, 0.5" to 1" long and wide
- singly or in pairs
- half of nut covered by a deep cap
Bark
- furrows and ridges
- gray-black color
Culture
- full sun
- difficult to transplant
- prefers acidic, sandy soils on the dry side based on natural occurrence
- seems less prone to chlorosis than pin oak
Landscape Use
- shade tree
- lawn tree
- should be saved in new construction
Liabilities
- considered hard to transplant
- very difficult to find in commerce
ID Features
- sinuses between lobes are "C"-shaped in comparison to Q. palustris, which has "U"-shaped sinuses
- acorns half-covered by a deep cap
- fall color late and red
Propagation
- by seed
Cultivars/Varieties
- none